An introduction to bookkeeping basics
Here are some basic bookkeeping concepts and definitions that you should know. They’re central to the methods and processes that a bookkeeper follows to create accurate accounts:
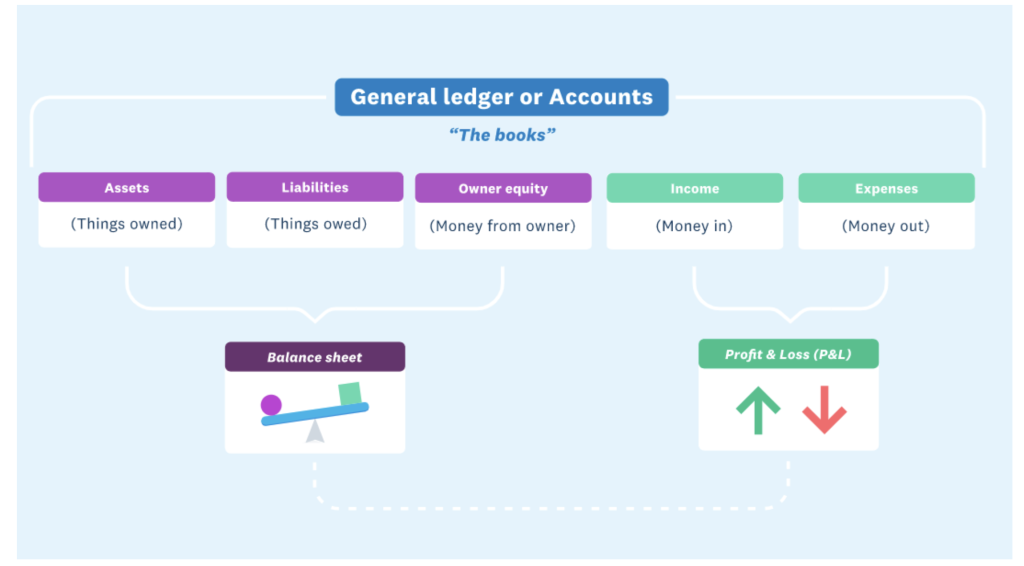
Ledger: The place where business transactions are recorded and categorised.
Accounts: The categories under which all business transactions fall:
- Assets: Things the business has bought and owns (or part-owns), inventory, and money owed to the business as accounts receivable.
- Liabilities: Amounts the business owes in unpaid bills, taxes, wages, or loans.
- Owner/shareholder equity: Money introduced and withdrawn by the owner or shareholders.
- Income: Money received (mostly from sales).
- Expenses: Money spent.
Financial statements: There are many financial statements but two main ones :
- The balance sheet lists the things your business owns and their value, plus the amounts your business owes.
- Profit and loss (P&L) totals the income and expenses for a set period of time and demonstrates how the business is trading.
Chart of accounts: Accounts are the basis of all transactional coding and double-entry bookkeeping. They help categorize types of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. They’re also called general ledger codes.
Journal entry: The name given to any record made in the accounts.
The difference between bookkeeping and accounting
Bookkeeping traditionally refers to the day-to-day upkeep of a business’s financial records. Bookkeepers used to simply gather and quality-check the information from which accounts were prepared. But their role has expanded over time, and we’ll look at how in the next chapter.
Accounting refers to the analysis, reporting, and summarising of the data that bookkeepers gather. Accounting reports give a picture of the financial performance of a business and determine how much tax is owed.
An accounting degree requires deep education and training in tax and other laws with which businesses need to comply, plus finance and business management. While some bookkeepers may have developed similar skills, that level of training isn’t required to be called a bookkeeper.








